ReentrantLock是排他锁,也就是同一时间也能有一个线程进行访问,而读写锁可以同一时间有多个读线程进行访问,而写线程访问时,所有读线程和其它写线程会被阻塞。读写锁维护了一对锁,一个读锁一个写锁,通过分离读写,使并发能力得到很大提高。
一、ReentrantReadWriteLock的特征 • 公平性:支持非公平(默认)和公平的获取锁方式,吞吐量还是非公平锁优于公平锁;
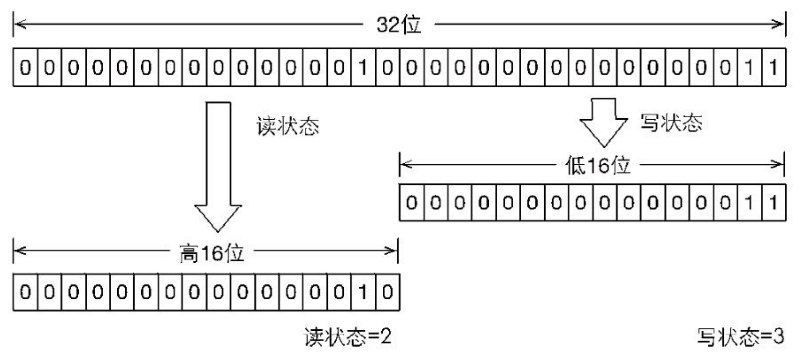
二、ReentrantReadWriteLock的实现 1、读写的状态(state变量)设计
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 sync内部类的代码为: static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16 ; static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT); static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1 ; static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1 ; static int sharedCount (int c) return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; } static int exclusiveCount (int c) return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
2、写锁的获取和释放:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); int w = exclusiveCount(c); if (c != 0 ) { if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) return false ; if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); } if ((w == 0 && writerShouldBlock(current)) || !compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires)) return false ; setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; }
1)、持有锁的线程数不为0(c=getState()),如果写线程数(w=0)为0,则读线程数不为0,并且当前线程不是占有锁的线程,返回失败。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) int nextc = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); if (exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0 ) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); setState(nextc); return true ; } else { setState(nextc); return false ; } }
释放的过程基本和独占锁ReentrantLock差不多。
3、读锁的获取和释放
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 protected final int tryAcquireShared (int unused) Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 && getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) return -1 ; if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); if (!readerShouldBlock(current) && compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId()) cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get(); rh.count++; return 1 ; } return fullTryAcquireShared(current); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 final int fullTryAcquireShared (Thread current) HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId()) rh = readHolds.get(); for (;;) { int c = getState(); int w = exclusiveCount(c); if ((w != 0 && getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) || ((rh.count | w) == 0 && readerShouldBlock(current))) return -1 ; if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { cachedHoldCounter = rh; rh.count++; return 1 ; } } }
以上获取读锁的代码流程为:
读锁的释放过程:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected final boolean tryReleaseShared (int unused) HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId()) rh = readHolds.get(); if (rh.tryDecrement() <= 0 ) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); for (;;) { int c = getState(); int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT; if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) return nextc == 0 ; } }
1)、获取读锁的计数器HoldCounter,然后减1;
另外同步器Sync的实现中还实现了tryReadLock和tryWriteLock两个方法,分别对应ReadLock的tryLock和WriteLock的tryLock。
三、ReentrantReadWriteLock的使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Cache static Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); static ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); static Lock rlock = rwl.readLock(); static Lock wlock = rwl.writeLock(); public static final Object get (String key) rlock.lock(); try { return map.get(key); }finally { rlock.unlock(); } } public static final void put (String key,Object value) wlock.lock(); try { map.put(key, value); }finally { wlock.unlock(); } } public static final void clear () wlock.lock(); try { map.clear(); }finally { wlock.unlock(); } } }